Forecast Models: Hurricane Forecast
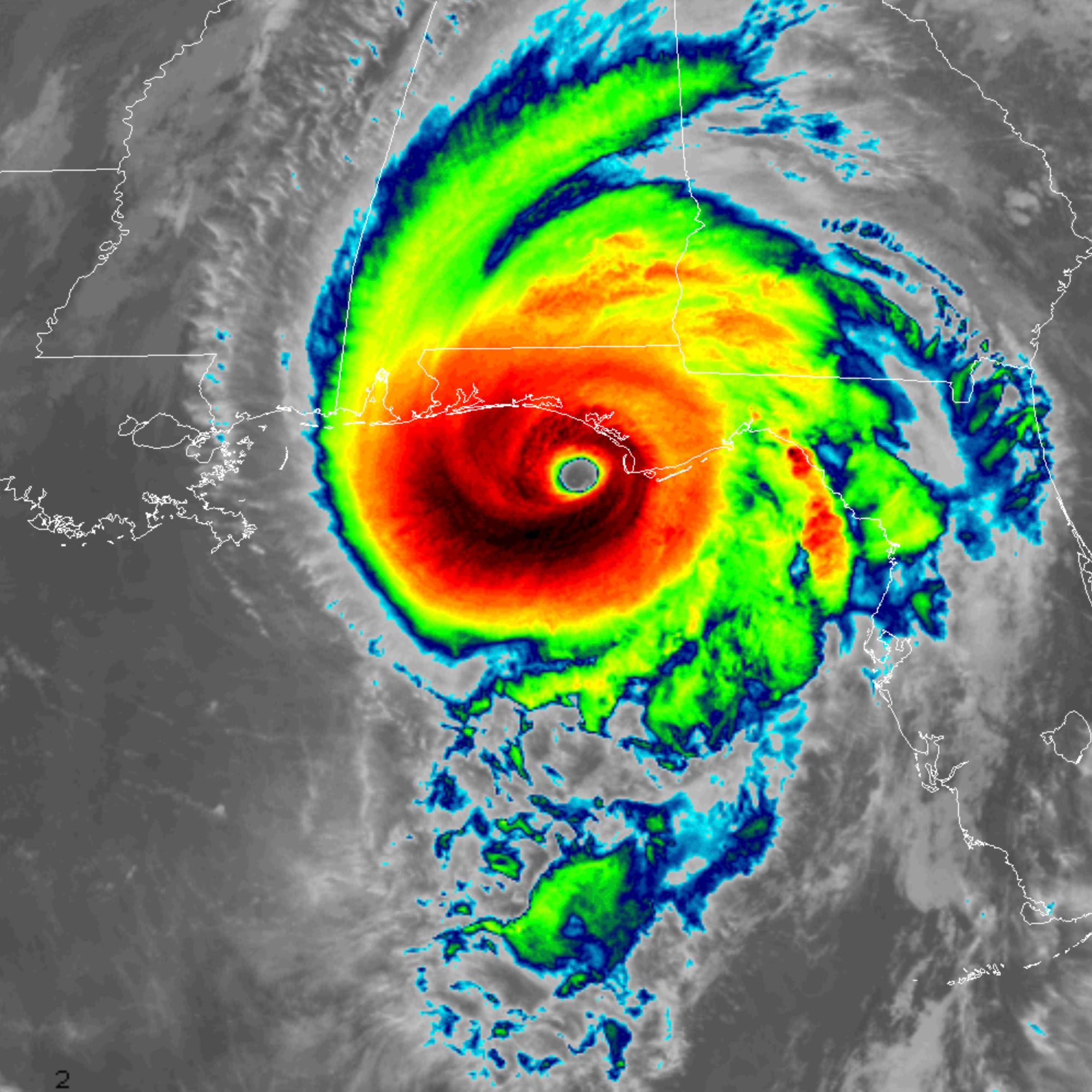
Hurricane forecast models are mathematical computer programs that use data from weather observations, satellites, and other sources to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes. There are two main types of hurricane forecast models: global models and regional models.
Monitoring hurricane forecasts is essential for staying prepared, especially during the peak season. As we keep a close eye on potential storms, one that warrants attention is Hurricane Beryl, which recently made landfall in Jamaica. Hurricane Beryl Jamaica provides updates on the storm’s impact, including damage assessments and relief efforts.
By staying informed about hurricane forecasts, we can take necessary precautions and ensure the safety of our communities.
Global models cover a large area, typically the entire globe, and are used to predict the general track of hurricanes. Regional models cover a smaller area, typically a specific region such as the Atlantic or Pacific Ocean, and are used to predict the more detailed track and intensity of hurricanes.
Hurricane forecasts are crucial for preparing for the potential impact of these powerful storms. By tracking the path of hurricanes, like Hurricane Beryl , meteorologists can provide timely warnings and guidance to help communities stay safe. These forecasts are essential for disaster preparedness and mitigation, enabling us to make informed decisions to protect lives and property.
Accuracy Rates
The accuracy of hurricane forecast models has improved significantly over the past few decades. The average error in track forecasts has decreased by about 50% since the 1970s. However, there are still challenges in forecasting hurricanes, especially in the short term.
One of the biggest challenges in hurricane forecasting is the lack of data. Hurricanes are relatively rare events, and there is not always enough data to accurately predict their behavior. Another challenge is the complexity of the atmosphere. Hurricanes are influenced by a number of factors, including wind shear, sea surface temperatures, and the Coriolis effect. These factors can interact in complex ways, making it difficult to predict the exact path and intensity of a hurricane.
Examples of Use
Hurricane forecast models are used by a variety of organizations, including the National Hurricane Center, the National Weather Service, and emergency management agencies. These organizations use the models to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes, and to issue warnings to the public.
Hurricane forecast models have helped to save lives and property. By providing early warnings, the models have given people time to evacuate from the path of hurricanes and to prepare for their impact.
Historical Hurricane Data

Hurricanes, a destructive force of nature, have left an indelible mark on history. To gain insights into their behavior and impact, it’s crucial to examine historical data.
Analyzing past hurricanes provides valuable information for understanding their frequency, intensity, and the regions they most commonly affect. This knowledge is essential for developing effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Most Significant Hurricanes in History
The table below summarizes some of the most significant hurricanes in history, along with their dates, locations, and impacts:
| Date | Hurricane | Location | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | Galveston Hurricane | Galveston, Texas | ~8,000-12,000 fatalities; widespread destruction |
| 1935 | Labor Day Hurricane | Florida Keys, Florida | ~408 fatalities; severe damage to infrastructure |
| 1969 | Hurricane Camille | Mississippi Gulf Coast | ~256 fatalities; widespread devastation |
| 1979 | Hurricane David | Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, United States | ~2,000 fatalities; significant damage |
| 1992 | Hurricane Andrew | Bahamas, Florida | ~65 fatalities; catastrophic damage |
| 2005 | Hurricane Katrina | Gulf Coast of the United States | ~1,833 fatalities; immense destruction |
| 2017 | Hurricane Maria | Puerto Rico, United States Virgin Islands | ~2,975 fatalities; widespread devastation |
Regions Most Frequently Affected by Hurricanes
Hurricanes primarily affect coastal regions, with some areas being more vulnerable than others. The regions most frequently impacted by hurricanes include:
- Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico
- Atlantic coast of the United States
- Eastern coast of Mexico
- Bay of Bengal
- South China Sea
Trends in Hurricane Frequency and Intensity Over Time
Historical data reveals trends in hurricane frequency and intensity. Over the past few decades, there has been an observed increase in the number of intense hurricanes (Category 3 or higher). This trend is attributed to factors such as:
- Rising sea levels
- Warmer ocean temperatures
- Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns
Understanding these trends is crucial for predicting future hurricane activity and implementing appropriate adaptation and mitigation measures.
Hurricane Preparedness
Hurricanes are powerful and potentially devastating storms that can cause widespread damage and loss of life. Being prepared for a hurricane is essential to ensure the safety of individuals and communities. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of hurricane preparedness measures, including evacuation plans, emergency kits, and staying informed during hurricanes.
Evacuation Plans
Evacuation is often the most critical aspect of hurricane preparedness. Having an evacuation plan in place before a hurricane strikes can save lives. Evacuation plans should include:
- Identification of evacuation routes and destinations
- Transportation arrangements
- Communication plans
- Pet evacuation plans
Emergency Kits, Hurricane forecast
Emergency kits are essential for providing basic necessities in the event of a hurricane. Emergency kits should include:
- Water (one gallon per person per day for at least three days)
- Food (non-perishable items such as canned goods and granola bars)
- First-aid kit
- Flashlights and extra batteries
- Whistle
- Cash
- Important documents (copies of passports, insurance cards, etc.)
Staying Informed
Staying informed during a hurricane is crucial for making informed decisions about evacuation and other safety measures. Information can be obtained from:
- Local news and weather stations
- National Hurricane Center
- Social media
- NOAA Weather Radio